Catalogue of Mesh Belt

Mesh Belt

KTC Conveyor Belts
■ Applications Include
General Features
The belts are produced and supplied customized for your specific needs with the following features
- A wide range of temperature resistance (-73 °C~ 260 °C)
- Ease use of adhesive material using outstanding feature of form changeability
- Stable level of length and width by using glass fiber material of good measurement stability
- Superior durability due to the minimum abrasion of belts due to impact resistance
- High UV rays resistance and thus can be used for UV drier
- Strong chemical resistance and long-term durability for chemical engineering process
- Preventing electrostatic charge and can be safely used for electronic and sewing manufacturing process
- Mesh format belts are available which can be used for drying process requiring permeability
- For other usages please make enquiries to the sales team of Hannam Corporation.
Applications include
| Applications |
Features |
Purposes |
Processing |
Processing materials |
Belts Used |
Packaging
Machines |
Heat resistant
Form changeability
Insulation
Flexibility |
Thermal lamination
Thermal contraction
Heat shield |
Hot plate
Hot air
Far infrared radiation |
Poly bag
cassette tape
Napkins
General food items |
8038,8058,8064
8108 |
| Printing Process |
Heat resistant
UV durability
Permeability |
Drying
Hardening
Adhesion |
Far infrared radiation
UV drying
Heat wave |
Printed materials
PCB Printing
Film Printing |
8108,8278,8338
8195,8255,8305,
8195AS,8255AS,8305AS |
Clothes
Sewing |
Insulation
Non-adhesiveness
Electronic (※2)
Wet proof |
Laminating
Fusing
Dyeing
Drying |
Hot plate
Heat wave
Steaming |
Felt ,
T-shirts
General clothes |
L-10,L-5
8159,8103AS,
8143AS,8305AS |
Food Processing
(※1) |
Heat resistant
Wetproof
Non-adhesiveness
Cold resistant
Permeability |
Drying,
Baking
Steaming
Thawing
Shaping
Transferring |
Far infrared radiation,
Hot plate,
Steaming,
Hot air,
High frequency |
Most food items |
8060,8110,8109
810K,817K
8308 |
| Rubber Products |
Heat resistant
Non-adhesiveness |
Transferring |
|
Rubber belt
General rubber products |
8108,8148 |
Synthetic
Resins |
Heat resistant
Non-adhesiveness |
Melting,
Molding,
Adhesive coating |
Far infrared radiation,
Hot air |
Urethane foam
Styrofoam, Carpets |
8159,8278,8338 |
Electronic
Parts |
electronic (※2)
Heat resistant,
Water proof
UV resistant
Permeability |
Parts Drying
Parts Cleaning
Hardening |
Far infrared radiation,
Hot plate,
Hot air,
UV drying |
PCB
Semi-conductor parts |
8033AS,8053AS
8103AS,8305AS |
- The belt products are complied with the food safety regulations of the USA FDA 21 CFR 177.1550 and has been approved by the accreditation authorities of USDA and NSF.
- In order to prevent static electricity the products contain conductivity paint.
■ Belts Splicing
Generally there are ten methods of belts splicing as illustrated on the following diagrams. Depending on situations, we may suggest more suitable method considering the conditions of facilities and belts, in which case a special technique can be utilized
■ Kinds Of Splice
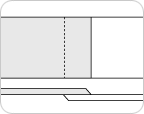
Scarf splice
Scarf splice uses a similar splicing method with the overlap splice method. It is also called as seamless splice because of the smooth edge finish. Splicing can be done on business trip while on-site manufacturing is not available.
|
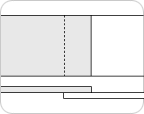
Overlap splice
The most common splicing method using thermosetting. Standard technique is to set the width of 25mm at an angle of 90°. But the width and angle can be adjusted according to usage. Belt splicing can be done on-site by a technician. Business trip manufacturing is also available.
|
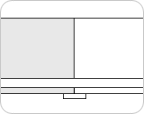
Butt Splice
A splicing method which allows smooth upper edge (surface contacting the material) finish. The lower part (surface contacting the pulley) is joined using thermosetting with the same fabric as the belt or different kinds of materials. It has a minor defect which is the relatively short durability because the contact surface is rubbed out easily.
|
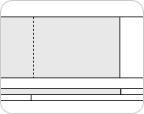
Two ply Laminated belt
An effective splicing method to splice the two-ply using thermosetting, removing the thickness difference
between the upper and lower fabric parts. Perfect for manufacturing process requiring extra smooth surface. Belt size should be within 100mm length due to the manufacturing difficulty.
|
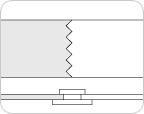
Sawtooth wave splice
This connection method is a method of heat-sealing the upper and lower reinforcements in the form of a saw blade using the blade.High strength of the joints as well as flexible benefits and the connections you can use a lot smoother surface also possible connections. we can perform a wide belt splicing in the field(up to 2,600mm).
|

PEEK spiral splice
This connection method is a method for connecting the belt mainly of the shape of the mesh. Flexibility and breathability of the joints in relation to the use of Kevlar reinforcement mesh are widely used in the mesh belt excellent.
|

Smart loop(Bullnose) splice
Very Similar to the PEEK spiral method. The loops do not require extra support materials as they are made by specially manufactured Para-aramid mesh. It has great permeability due to the simple sewing process. However, it is less flexible compared with PEEK and the process connecting with the pins can be slightly complicated.
|

Heavy duty fabric splice
Using Para-aramid fabric as a support material for the connected parts and instead of metal pin, FRP pin is utilized making it perfect for high frequency oven belt.
|
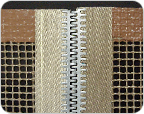
Allgator splice
As a splicing method using connecting metal loops which look like an alligator. It has been widely used in the past but now less popular.
|
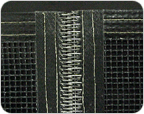
Clipper laced splice
Very similar to the alligator splice method except of the shape of the connecting loops.
|
Sewing Industrial Lamination Belts
■ Lamination Belts
Lamination belts have the following excellent features compared with other one-ply glass or Para-aramid belts :
- Flexible joining parts and outstanding durability
- Extra thin joining parts and minimized occurrence of transferring in the joining parts
- Flexibility of joining parts preventing meandering and superior operation stability
- Excellent form changeability and top surface quality
- Excellent antistatic feature
- Can be used continuously at temperatures between -73℃ and 260℃
- Can be manufactured with the width up to 2.4m
■ Types of Basic Style
- L-6 : Total thickness 0.15mm, (Nominal thickness 0.075mm x 2ply)
- L-9 : Total thickness 0.23mm, (Nominal thickness 0.075mm x 3ply)
- L-10 : Total thickness 0.25mm, (Nominal thickness 0.125mm x 2ply)
- L-15 : Total thickness 0.38mm, (Nominal thickness 0.125mm x 3ply)
- Processing the edge is available (wrap or strip)
- Belt guide is available for one side or both (Para-aramid profile or buttons)
■ Spliced Parts Features
Previous belt splice has several defects such as stiffness from two-ply and meandering of spliced parts, which lead to poor quality. To eliminate these defects, this product use thermosetting method on the thin PTFE coated glass fabric two or three fold, which improve the flexibility of spliced parts and minimize the meandering.
Belt Specification
| Series No |
Standard
width
(m) |
Nominal thickness
(μm) |
Weight
(g/㎡) |
PTFE Content
(%) |
Tensile strength
(N/5㎝) |
Dielectric breakdown
(V) |
Surface resistivity
(MΩ) |
Remark |
| Electrical Grade |
| H8060 |
1.0, 1.5 |
146 |
320 |
67 |
1300 |
5500 |
- |
|
| H8110-3 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
275 |
630 |
68 |
2600 |
6000 |
- |
|
| Premium Grade |
| H8059 |
1.0, 1.5 |
128 |
280 |
61 |
1300 |
4500 |
- |
|
| H8069 |
1.0, 1.5 |
142 |
309 |
65 |
1300 |
5000 |
- |
|
| H8109 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0 |
245 |
534 |
61 |
2300 |
5500 |
- |
|
| H8109-3 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
245 |
534 |
61 |
2300 |
5500 |
- |
|
| H8119-3 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
270 |
600 |
66 |
2600 |
5600 |
- |
|
| H8149 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
350 |
735 |
60 |
4200 |
4000 |
- |
|
| H8279MG |
1.5, 2.6 |
840 |
1200 |
51 |
4500 |
3000 |
- |
|
| Standard Grade |
| H8058 |
1.0, 1.5 |
122 |
265 |
59 |
1300 |
4000 |
- |
|
| H8068 |
1.0, 1.5 |
138 |
296 |
63 |
1300 |
4800 |
- |
|
| H8108 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0 |
235 |
490 |
58 |
2300 |
5300 |
- |
|
| H8108-3 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
235 |
490 |
58 |
2600 |
5300 |
- |
|
| H8148 |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
340 |
680 |
57 |
4200 |
3800 |
- |
|
| H8208 |
2.0 |
450 |
880 |
54 |
4500 |
4000 |
- |
|
| H8278TC |
1.5, 2.6 |
670 |
950 |
35 |
4000 |
2000 |
- |
|
| H8278S |
1.5, 2.6 |
680 |
1100 |
44 |
4500 |
5000 |
- |
|
| Open Mesh |
| H8195P |
1.55, 1.8 |
670 |
520 |
21 |
3500 |
- |
- |
|
| H8225 |
2.5, 2.7 |
770 |
445 |
26 |
1900 |
- |
- |
|
| H8305 |
2.0, 2.5, 2.65, 3.2, 4.8 |
980 |
460 |
32 |
2400 |
- |
- |
|
| H8305AS |
2.0, 2.5, 2.65, 3.2, 4.8 |
950 |
460 |
32 |
1800 |
- |
- |
|
| H8305K |
2.7 |
770 |
310 |
46 |
4000 |
- |
- |
Kevlar |
| H8305KG |
2.8, 3.3 |
1250 |
644 |
35 |
5500 |
- |
- |
Kevlar/Glass |
| H8305NG |
2.0, 2.9 |
1800 |
680 |
41 |
1800 |
- |
- |
Nomex/Glass |
| Crease and Tear Resistant |
| H8054 |
1.0 |
126 |
255 |
57 |
1300 |
2500 |
- |
|
| H8064 |
1.0 |
145 |
296 |
63 |
1300 |
3500 |
- |
|
| H8104 |
1.0, 1.5 |
240 |
490 |
59 |
1900 |
4000 |
- |
|
| Anti-static Grade |
| H8053AS |
1.0 |
125 |
255 |
58 |
1300 |
- |
<10 |
|
| H8063AS |
1.0 |
145 |
296 |
63 |
1300 |
- |
<10 |
|
| H8103AS |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0 |
235 |
490 |
58 |
2300 |
- |
<10 |
|
| H8103-3AS |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
235 |
490 |
58 |
2300 |
- |
<10 |
|
| H8143AS |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
345 |
700 |
58 |
4200 |
- |
<10 |
|
| H8153AS |
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 |
350 |
735 |
60 |
4200 |
- |
<10 |
|
| Kevlar fabrics |
| H815K |
2 |
370 |
475 |
52 |
6500 |
2000 |
- |
Kevlar |
| H815KAS |
2 |
370 |
570 |
59 |
6500 |
- |
<10 |
Kevlar |
| H817K-1 |
1.6 |
430 |
720 |
63 |
4000 |
4500 |
- |
Kevlar |
| H817KAS |
1.6 |
425 |
660 |
59 |
4000 |
- |
<10 |
Kevlar |
Laminated Belt
■ Laminated Belt
Laminated Belt or Composite Belt has been created to eliminate several defects of previous belt splice, such as stiffness from two-ply and meandering of spliced parts, which lead to poor quality. Its utmost features include the improved flexibility of spliced parts and reduction of the meandering incidence of spliced parts through thermosetting method. This is done on the thin PTFE coated glass fabric by two or three fold.
■ Types of Laminated Belt
- L-6 : Nominal 0.075mm PTFE Glass Fabric 2 ply - Thickness 0.15mm
- L-9 : Nominal 0.075mm PTFE Glass Fabric 3 ply - Thickness 0.23mm
- L-10 : Nominal 0.125mm PTFE Glass Fabric 2 ply - Thickness 0.25mm
- L-15 : Nominal 0.125mm PTFE Glass Fabric 3 ply - Thickness 0.38mm
■ Benefits
- Flexible spliced parts and outstanding durability
Extra thin joining parts and minimal occurrence of meandering in the joining parts
- Flexibility of joining parts preventing meandering and superior operation stability
- Excellent variance and top surface quality
- Excellent antistatic feature
- Can be used continuously at temperatures between -73℃ and 260℃
■ Product Standards
Maximum width and length of available belt
- Width : up to 2000mm
- Length : No limit
Temperature for continuous usage
-73℃ ~ 260℃
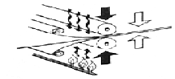
Splicing method
For splicing method of belts please see the illustration on the left. It has the same sealing strength as the joining parts and main body fabrics when completed. This method enables smooth touch and minimum thickness difference in the spliced parts.
Belt Edge Supporting Technique
In order to prevent the ply fray and support the machinery strength, one of the following three methods can be selected and applied when the belt is installed and operated.
-
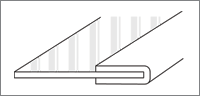 Envelope Reinforcing Method
Envelope Reinforcing Method
This method puts support materials (fabric or PTFE film) on the edge with thermosetting method. Sewing work is also available on the covered parts depending on client's needs.
-
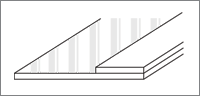 Laminate Method
Laminate Method
As a method to attach buttons and others on the edge, laminate method fuses PTFE coated G / F with specified width on the upper, lower or both sides.
-
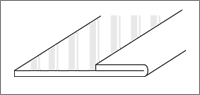 Fold over Method
Fold over Method
This method is a method to fold the belt itself Fabric the edge portion with a constant width reinforced by heat fusion. The PTFE coated G / F can not use this method para-aramid (Para-aramid) or a meta- aramid (Meta-aramid) belt only.
Common Edge Support Materials
Safety equipments can be attached on one side or both sides to prevent the meandering and the operation stability
- 5mil CR type Glass Fabric
- 6mil Para-aramid Fabric
- 3.5mil PTFE Film
※ mil : 1/1,000 inch =25.4㎛
Prevention of Belts Meandering
Pin, grommet or Para-aramid profile can be attached, which will pass through the grooved pulley and thus preventing the belt from transferring on one or both edge. Applicable usually for under the width of 1,000 mm.
Comparison of Laminated PTFE Belt and Ordinary PTFE Belt
| Ordinary PTFE Belt |
Laminated PTFE Belt |
| Difficult to adjust the meandering |
Easy to adjust the meandering |
| Spliced parts weakening due to gradual reduce of flexibility |
Spliced parts maintaining strength with great flexibility |
| Spliced parts showing marks |
Spliced parts showing minimal marks due to having similar thickness with belts |
| Thick belts having coarse finish due to weaving pattern |
Presenting perfect smoothness regardless of thickness |
| Weak sealing strength |
Excellent sealing strength |
| Low heat resistance |
Superior heat resistance |
| Belts easily damaged when slide-away occurs |
Rare occurrence of slide-away |
| Strong belt tension can cause belts twisted |
Able to endure strong tension without twist |
| Only one surface type for each product |
Several surface types available
Example : AS/non AS, food quality /drive quality |
| Short durability, particularly the contacting parts |
Long-term durability (particularly the contacting parts) |
| Soft surface worn out easily |
Strong and firm surface with high-pressure processing |
Type Physical Properties of Laminated PTFE Belt
| Product |
L6 |
L9 |
L10 |
L15 |
| Reinforcing Fabric |
2Ply Glass Fabric |
3Ply Glass Fabric |
2Ply Glass Fabric |
3Ply Glass Fabric |
| Coating Type |
PTFE with graphite filler |
PTFE with graphite filler |
PTFE with graphite filler |
PTFE with graphite filler |
| Interlayer |
PTFE |
PTFE |
PTFE |
PTFE |
| S.G.(Relative Density) |
2.16 |
2.16 |
2.16 |
2.16 |
| % Coating |
66 |
66 |
58 |
58 |
| Tensile Warp(N/5cm)Min |
1000 |
1650 |
1600 |
2500 |
| Tensile Weft(N/5cm)Min |
800 |
1450 |
1400 |
2200 |
| Tear Strength(BS)Warp(N) Min. |
14 |
25 |
24 |
38 |
| Tear Strength(BS)Weft(N) Min. |
11 |
20 |
18 |
28 |
| %Elongation @break warp Min. |
2.5 |
2.2 |
3.2 |
3.0 |
| %Elongation @break weft Min. |
3.0 |
2.7 |
3.5 |
3.2 |
| Weight (g/sqm)+/-5% |
292 |
438 |
530 |
811 |
| Nominal Thickness(mm) |
0.15 |
0.23 |
0.25 |
0.38 |
| Overlap thickness(mm)_Nominal |
0.23 |
0.30 |
0.38 |
0.51 |
| Surface Resistivity (m-ohms) Min. |
<10 |
<10 |
<10 |
<10 |
| Operating Temp.(deg. C) |
-73 ~ 260 |
-73 ~ 260 |
-73 ~ 260 |
-73 ~ 260 |
Application of Laminated Belt
- Textiles - fusing and laminating
- PVC processing
- Carpet manufacturing
- Timber, textiles & plastic board production
- Plastic & rubber form production
- Plastic & rubber molding
- Electronic, semi-conductors line transporting facilities
|